Impact of Analytics on Meeting Productivity
Discover how analytics can revolutionize meeting productivity by optimizing schedules, enhancing engagement, and driving strategic decision-making...
Optimize your organization's meetings with Strategic Meeting Management. Learn how to transform meetings from time-draining activities into strategic assets that drive productivity and alignment.
Meetings are one of the most expensive, high-frequency activities inside any organization, and yet, they’re often the least managed.
Time is spent without scrutiny. Calendars fill without oversight. And what starts as collaboration quickly becomes an operational liability: overloaded teams, distracted employees, rising salary costs tied up in low-value discussions, and slower decision-making across the board.
While finance teams track spend and IT teams manage infrastructure, meetings often slip through the cracks. There's no centralized policy, no governance layer, and little data to understand what's working or what's wasting time.
For operations leaders, this represents a critical blind spot. Meetings affect every part of the business, from alignment and execution to morale and margin. It’s time they were treated like any other core system: measured, optimized, and managed with intention.
Strategic Meeting Management (SMM) is a structured, data-informed approach to planning, executing, and evaluating meetings across an organization. It encompasses standardized processes, clear policies, and analytics to ensure meetings align with business objectives and deliver measurable value.
Unlike ad hoc or decentralized scheduling, where meetings are organized without consistent guidelines, SMM treats meetings as an operational system. This shift from individual behaviors to organizational strategy enables companies to optimize time, reduce costs, and enhance collaboration.
By adopting SMM, organizations can transform meetings from time-consuming obligations into strategic tools that drive productivity and align with corporate goals.
In many organizations, meetings are scheduled without a standardized approach, leading to a decentralized meeting culture. Each team or individual may have their own methods for scheduling, conducting, and following up on meetings. This lack of uniformity can result in inefficiencies and misalignments across the company.
Without centralized oversight:
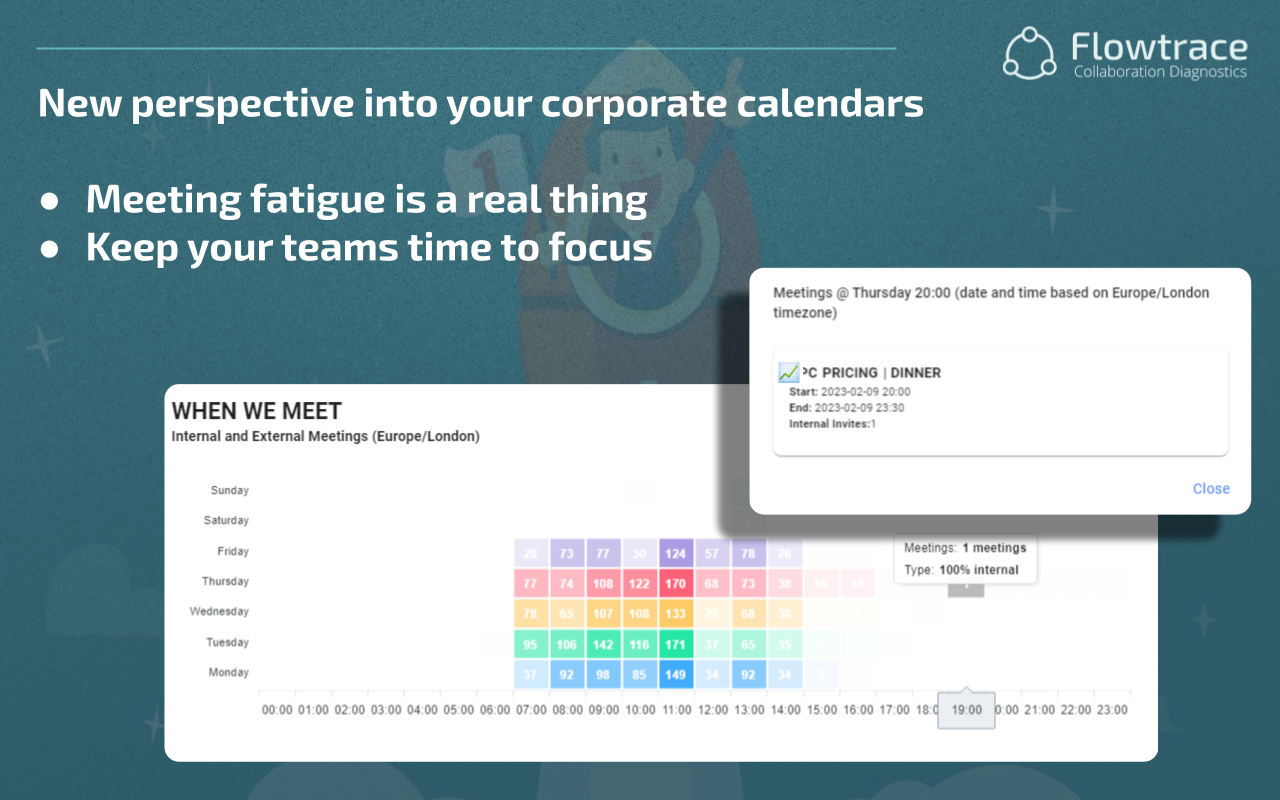
Implementing a strategic meeting management system can address these challenges by introducing standardized practices and providing tools for better oversight. For instance, adopting meeting analytics can help organizations track meeting frequencies, durations, and participant engagement levels.
Additionally, establishing meeting types and their purposes ensures that each meeting has a clear objective and structure, reducing redundancy and enhancing effectiveness.
Moreover, understanding the cost implications of meetings can motivate teams to be more judicious with their scheduling, ensuring that meetings are necessary and productive.
By transitioning from a decentralized to a centralized meeting culture, organizations can enhance collaboration, improve time management, and align meetings more closely with strategic objectives
An effective Strategic Meeting Management (SMM) framework rests on five key pillars, each supported by policy, process, and data:
Define standardized meeting types, decision-making sessions, brainstorming workshops, status updates, and 1:1s, each with clear expected outcomes and formats (sync vs. async). Use your meeting taxonomy guidelines to ensure every session has a purpose.
Establish organization-wide rules for default durations, buffer times between appointments, maximum invitee counts, and recurrence limits. Applying these duration and buffer rules prevents calendar overload and keeps meetings lean.

Gatekeep low-value meetings by requiring a published agenda and clear objectives before any invite goes out. Automated agenda validation ensures only well-scoped gatherings make the cut.
Track meeting volume, participation rates, cost per session, and policy adherence across the company. Leveraging comprehensive meeting analytics uncovers hidden inefficiencies and opportunities for consolidation.
Close the loop with pulse surveys or post-meeting evaluations to gauge effectiveness and gather qualitative insights. Embedding regular meeting feedback surveys turns subjective impressions into actionable data.
Putting these components in place isn’t optional, it's essential. After all, according to Atlassian, the average professional attends 62 meetings per month, and 50% of workers say meetings are the biggest waste of time. Systematic SMM transforms meetings from time drains into strategic assets.
Operations teams are uniquely positioned to transform meeting culture from a decentralized, ad hoc process into a structured, data-driven system. By implementing a centralized framework, ops can ensure meetings are purposeful, efficient, and aligned with organizational goals.
Utilize tools like Google Calendar and Outlook in conjunction with Flowtrace's calendar integrations to set organization-wide defaults. This includes standardizing meeting durations, setting buffer times, and limiting the number of participants to prevent overload.
Implement meeting taxonomy guidelines to define clear meeting types, such as decision-making sessions, brainstorming meetings, and status updates. Standardized templates ensure consistency and clarity across all meetings.
Leverage agenda validation tools to prompt organizers to include agendas and objectives before scheduling meetings. Automated nudges can also alert when meetings exceed participant limits or lack necessary documentation.
Use meeting analytics dashboards to monitor key metrics such as total meeting hours, frequency of recurring meetings, and participant engagement levels. Regular reporting helps identify patterns and areas for improvement.
By adopting these strategies, operations teams can significantly reduce meeting inefficiencies. Considering that employees spend an average of 11.3 hours in meetings each week, accounting for 28.3% of their workweek , optimizing meeting practices is crucial for enhancing productivity and employee satisfaction
Implementing a strategic approach to meeting management unlocks wide-reaching organizational gains, beyond just better calendars.
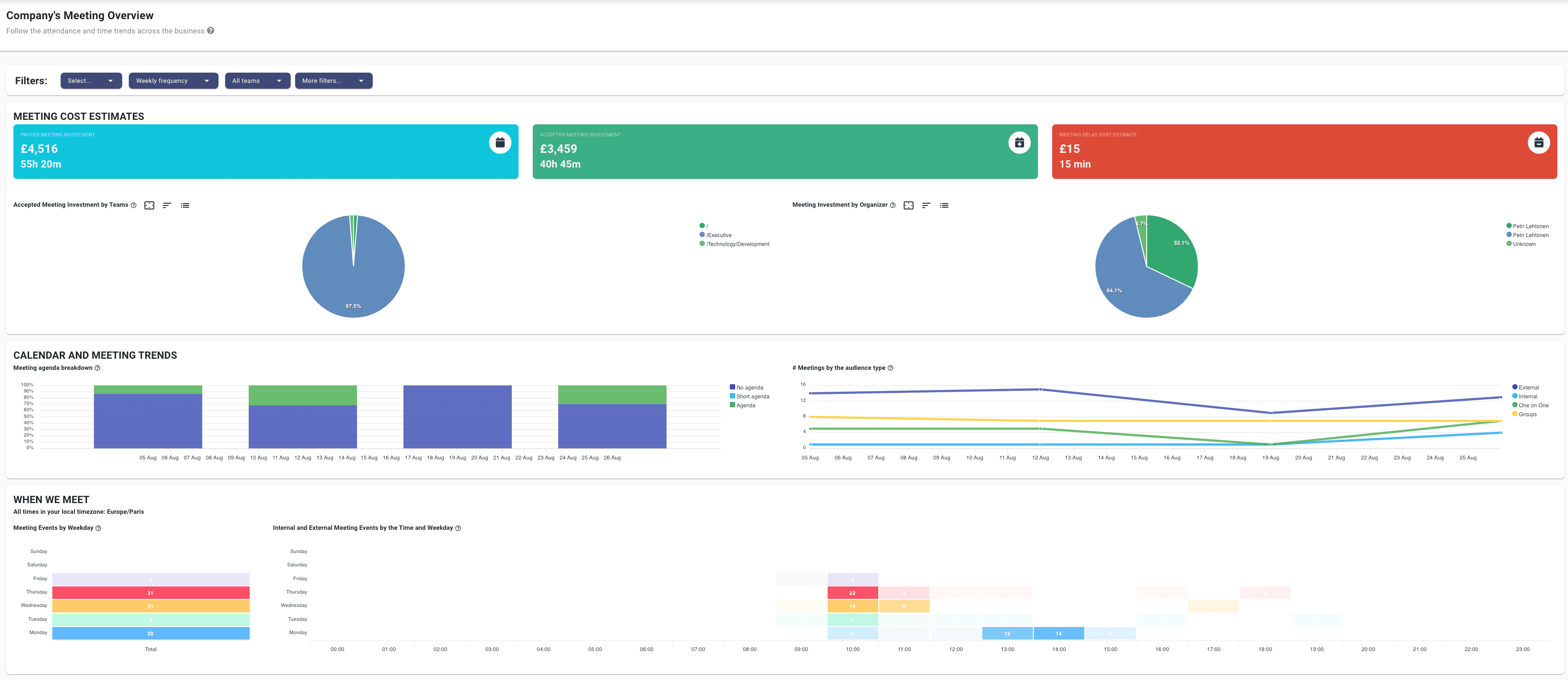
By using tools like meeting analytics and Google Calendar dashboards, companies gain visibility into meeting volume and overlap, allowing them to eliminate redundant sessions and protect time for focused work.
Enforcing meeting rules for calendar optimization ensures every team follows the same standards for agendas, durations, and invitee limits. This consistency leads to more intentional scheduling and better meeting hygiene.
Reducing meeting bloat and increasing transparency creates more space for autonomy and collaboration. Tools like meeting feedback analytics help organizations keep a pulse on meeting effectiveness from the participant’s point of view.
When you can track meeting costs by department or function, it's easier to make decisions about where to scale back. Centralized visibility helps finance and ops teams quantify the ROI of time spent in meetings and reclaim efficiency.
Rolling out a Strategic Meeting Management framework doesn’t require an all-at-once overhaul. Here’s how organizations can implement it in stages with measurable results:
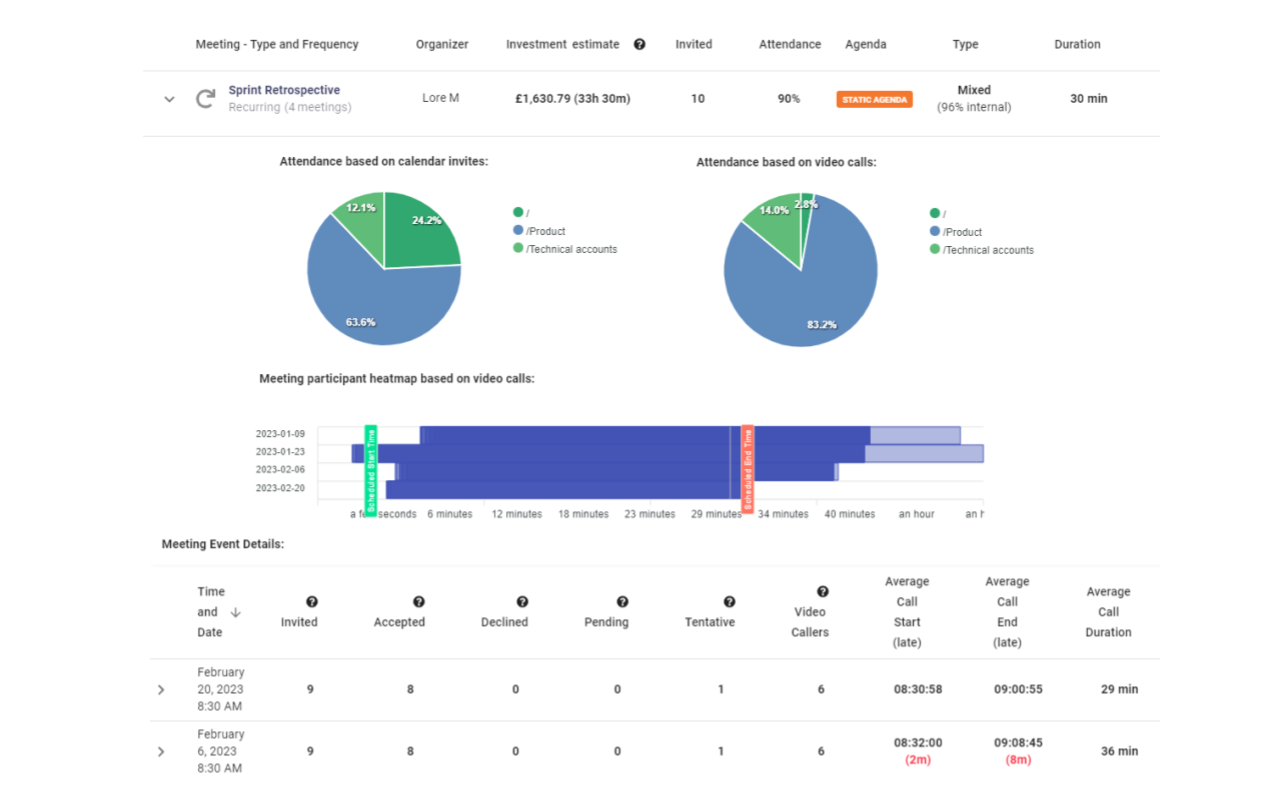
Audit existing meeting behavior (baseline analytics):
Start by conducting a calendar audit to understand how meetings are currently distributed across teams, roles, and functions. Use meeting analytics dashboards to create a performance baseline.
Define policies in collaboration with leadership and team leads:
Work with department heads to define meeting rules around duration, agenda requirements, and maximum invite counts. Tailor policies to support company values like async-first or deep work.
Configure calendar integrations and dashboard visibility:
Deploy Google Calendar or Outlook integrations and activate team-level dashboards for transparency. Empower employees and managers to track their own time usage and costs.
Run a pilot with selected teams:
Choose teams with diverse workflows (e.g., product, sales, ops) and test your policies in a controlled environment. Use meeting feedback analytics to gather qualitative input.
Company-wide rollout + change management
Expand policies org-wide with leadership backing, documentation, and regular check-ins. Make meeting optimization a recurring item in team retros or ops reviews.
Ongoing refinement based on usage data
Track improvement areas with data-driven insights. Refine defaults, update nudges, and review performance trends quarterly.
To manage meetings effectively at scale, organizations need to track the right indicators, not vanity metrics, but those that reflect alignment, efficiency, and cost.

Strategic Meeting Management isn’t a theoretical concept, it’s a practical framework that operations teams are already starting to adopt across industries. Here's how it looks in action:
Using analytics to reduce unnecessary recurring meetings

Many organizations begin by conducting a baseline audit of their meeting load using analytics dashboards. This reveals recurring meetings that have outlived their usefulness or involve too many attendees. By reviewing and streamlining these series, teams often free up hours of calendar time each week.
Establishing policy-driven scheduling habits
With standardized rules around meeting length, required agendas, and invite limits, companies create consistency across departments. This reduces scheduling friction and helps prevent overload, especially for roles most vulnerable to calendar bloat.
Shifting culture through visibility and feedback
Dashboards and subtle nudges give teams visibility into how they spend time, something most people rarely consider. When employees see their own meeting behavior and trends, they’re more likely to self-correct, leading to a healthier, more intentional meeting culture over time.
This is what strategic meeting management looks like in practice: not drastic overhauls, but incremental, data-informed improvements that scale across teams.
If your team is serious about productivity, time efficiency, and culture, then meetings need the same level of governance as budgets, tools, or hiring. With the right systems, clear policies, and company-wide analytics, ops leaders can finally take control of one of the most expensive and overlooked layers of the workplace: how time gets spent. It's time to turn meetings into a strategic advantage.
Discover how analytics can revolutionize meeting productivity by optimizing schedules, enhancing engagement, and driving strategic decision-making...
Learn how to fix unproductive meetings and enhance organizational productivity with strategic planning, effective meeting practices, and innovative...
Enhance productivity and decision-making with strategic meeting management. Learn key components, best practices, and solutions for effective...