Understanding Company Meeting Costs
Understanding and managing company meeting costs is essential for organizational efficiency and financial health. Explore the impact of direct,...
Discover indirect costs of meetings, from employee downtime to regulatory expenses, and learn how managing these indirect costs can boost organizational efficiency and financial health.
In organizational management, costs associated with meetings can be categorized into direct and indirect costs. Direct costs include visible expenses like meeting spaces, technology, catering, travel, and accommodation. These costs are straightforward and easy to quantify.
Indirect costs, however, are less visible but significantly impact an organization's efficiency and financial health. These include employee downtime, lost productivity, overtime, regulatory costs, opportunity costs, and the impact on employee morale. Indirect costs can accumulate over time, affecting the overall productivity and bottom line of the organization.
Understanding and managing indirect costs in meetings is crucial for improving meeting efficiency and organizational productivity. Identifying and addressing these hidden costs can streamline meeting processes, reduce unnecessary expenses, and enhance employee satisfaction and engagement, ultimately benefiting the organization's financial health.
Indirect costs are crucial to consider because they can significantly impact an organization's overall financial health. Unlike direct costs, which are easily identifiable and accounted for, indirect costs are often hidden and accumulate over time, affecting productivity and efficiency.
For instance, employee downtime during meetings means less time spent on productive tasks, leading to lower overall output. Additionally, high levels of employee burnout, driven by excessive or poorly managed meetings, can lead to increased absenteeism, reduced productivity, and higher turnover rates, which collectively strain the organization's resources and bottom line.
According to the Harvard Business Review, the cumulative effect of unproductive meetings can be staggering, with some estimates suggesting that poor meeting practices cost businesses billions in lost productivity annually. Addressing these hidden costs is essential to improving overall efficiency and productivity. Indirect costs include various hidden expenses that can add up substantially. For example:
Employee downtime refers to periods during which employees are not actively engaged in productive work tasks. When employees spend significant amounts of time in meetings, especially those that are frequent or lengthy, it directly impacts their ability to perform their regular duties. This time away from core tasks can lead to several productivity issues:

Understanding the hourly cost of employees in meetings is crucial for evaluating the financial impact of these sessions. To calculate the hourly cost:
Determine Hourly Wage: Start by identifying the hourly wage of each meeting participant. This can be done by dividing the annual salary by the total number of working hours in a year (typically 2,080 hours for a full-time employee).
Example: For an employee with an annual salary of £80,000, the hourly wage would be calculated as follows:
Hourly Wage = 2,080 / £80,000 ≈ £38.46
Multiply by Meeting Duration: Multiply the hourly wage by the duration of the meeting to find the cost per employee per meeting.
Example: For a two-hour meeting, the cost for one employee would be:
Cost per Meeting = £38.46 × 2 = £76.92
Sum Across Participants: To find the total cost of the meeting, sum the individual costs for all participants.
Example: If 10 employees attend a two-hour meeting:
Total Cost = £76.92 × 10 = £769.20
When meetings extend beyond regular working hours, they can incur additional costs due to overtime pay. Overtime is typically calculated at 1.5 times the regular hourly rate for non-exempt employees.
Identify Overtime Rate: Calculate the overtime rate by multiplying the regular hourly rate by 1.5.
Example: For an hourly rate of £38.46, the overtime rate would be:
Overtime Rate = £38.46 × 1.5 = £57.69
Calculate Overtime Costs: Multiply the overtime rate by the number of overtime hours worked.
Example: If a meeting extends one hour beyond regular hours, the cost per employee would be:
Overtime Cost = £57.69 × 1 = £57.69
Sum Across Participants: As with regular hours, sum the individual overtime costs for all participants to find the total additional cost.
Example: If 10 employees stay one extra hour:
Total Overtime Cost = £57.69 × 10 = £576.90
Regular Team Meetings: These often involve multiple employees and recur frequently.
For a weekly one-hour meeting with 10 employees each earning $38.46 per hour:
Weekly Cost = £38.46 × 10 = £384.60
Over a year, this adds up to:
Annual Cost = £384.60 × 52 = £20,019.20
Extended Strategy Sessions: These can be more costly due to their length and the seniority of participants. A four-hour strategy meeting with 5 executives each earning £100 per hour would cost:
Meeting Cost = £100 × 4 × 5 = £2,000
Ad Hoc Emergency Meetings: Often unplanned, these can incur additional costs, especially if they extend beyond regular working hours. A two-hour emergency meeting with 8 employees, half of whom earn overtime, could cost:
Regular Hours Cost = £38.46 × 2 × 4 = £307.68
Overtime Cost = £57.69 × 2 × 4 = £461.52
Total Cost = £307.68 + £461.52 = £769.20
Regulatory costs are expenses incurred by organizations to comply with laws, regulations, and standards set by governmental bodies or industry authorities. Regulatory costs are essential to ensure that organizations operate legally and ethically, but they can also represent a significant financial burden.
For example, with the rise of data protection regulations like GDPR in Europe and CCPA in California, technology companies must ensure they handle user data in compliance with these laws. Regular meetings to discuss data protection strategies and compliance are necessary.
Regulatory costs, while necessary for legal and ethical operations, can be substantial. Meetings to address these requirements add to these costs but are essential for maintaining compliance and avoiding penalties. By understanding and managing these costs, organizations can ensure efficient compliance with regulatory standards while minimizing financial impact.
Opportunity costs represent the potential benefits that an organization misses out on when resources, such as time and personnel, are allocated to less productive activities instead of more valuable tasks.
In the context of meetings, opportunity costs refer to the loss of productive work that employees could have completed if they were not attending meetings. This concept highlights the trade-offs between attending meetings and performing other essential duties that could contribute more directly to the organization's goals.
Delayed Project Timelines
Frequent meetings can disrupt the workflow, causing delays in project timelines. When employees spend excessive time in meetings, the actual time available for project work diminishes, leading to missed deadlines and extended project durations.
According to a study by the Harvard Business Review, unproductive meetings cost U.S. companies an estimated $37 billion annually due to wasted time and resources.
Reduced Quality of Work
The constant interruption caused by meetings can lead to fragmented work and reduced focus, potentially lowering the quality of work produced. Employees might rush through tasks to compensate for lost time, leading to errors and subpar outcomes.
Employee Burnout and Turnover
The pressure to attend numerous meetings while keeping up with regular duties can contribute to employee burnout. Over time, this can lead to higher turnover rates, as employees seek better work-life balance and more fulfilling job roles elsewhere.
Stunted Innovation
Innovation requires dedicated time for brainstorming, experimentation, and iteration. Excessive meetings can stifle creativity by leaving little room for these critical activities. Over time, this can hinder the organization’s ability to innovate and stay competitive.
Excessive or poorly managed meetings can have a detrimental effect on employee morale. When meetings are frequent, lengthy, or unproductive, they can lead to frustration and disengagement among employees. Here are some specific ways in which such meetings impact morale:
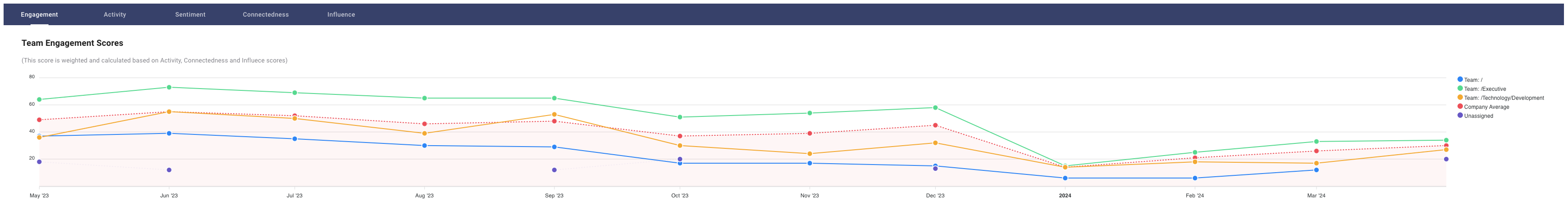
Employee engagement is directly linked to productivity. Engaged employees are more likely to be motivated, committed, and willing to go the extra mile to achieve organizational goals. Conversely, disengaged employees are less productive, more likely to take sick leave, and have higher turnover rates.
Decreased morale can lead to higher turnover rates, which carry significant costs for organizations. These costs include:
In-person meetings often necessitate travel and accommodation for participants, which can incur significant expenses. These costs include airfare, hotel stays, meals, local transportation, and other incidental expenses. For organizations with distributed teams or clients, the cumulative travel and accommodation expenses can quickly escalate, impacting the budget.
For large organizations, these travel and accommodation costs can add up significantly, especially if meetings are frequent or involve multiple participants from different locations. For example: A company organizing a quarterly in-person meeting for its regional managers may incur the following costs:
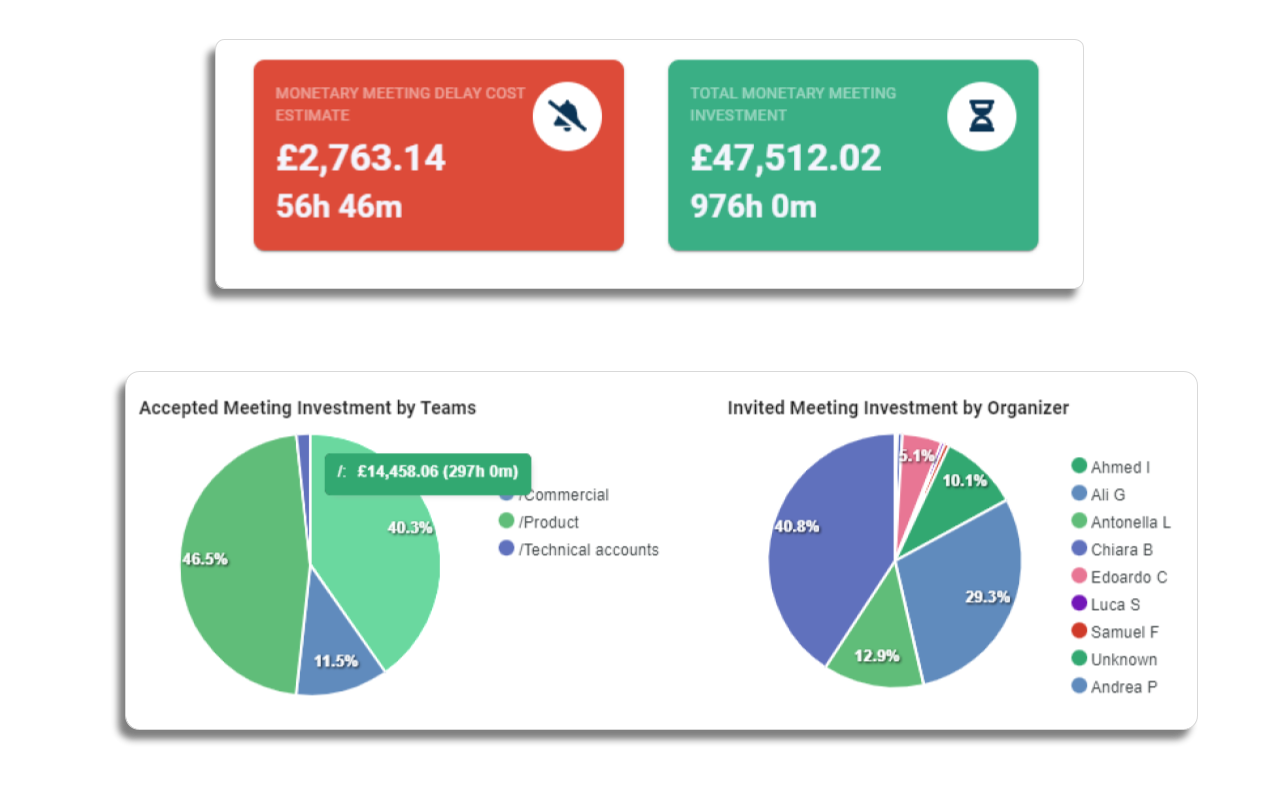
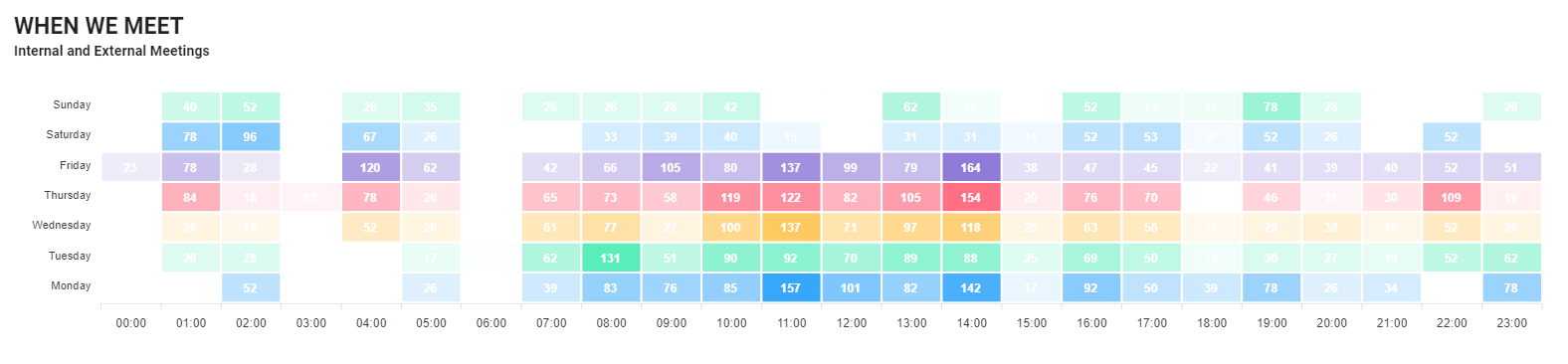
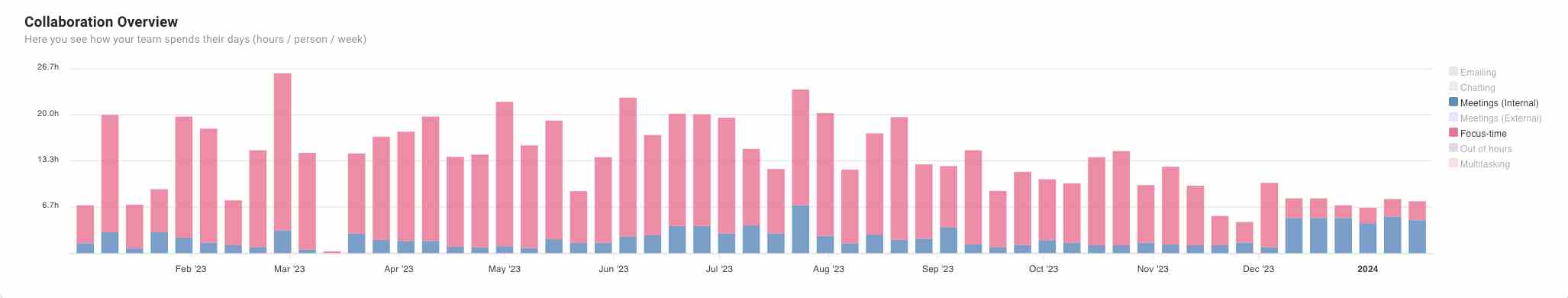
Meeting analytics provides a data-driven approach to understanding and improving meeting practices within an organization. By collecting and analyzing various metrics related to meetings, organizations can identify inefficiencies that contribute to indirect costs such as wasted time, decreased productivity, and low engagement.
Analytics can uncover patterns and trends that may not be immediately visible, allowing organizations to make informed decisions about how to streamline meetings and reduce associated costs.
Implementing effective strategies to mitigate indirect costs associated with meetings is crucial for enhancing organizational efficiency and productivity. Leveraging tools like Flowtrace and meeting analytics can provide valuable insights and help streamline meeting practices.
.png?width=1366&height=768&name=Outlook%20Add%20In%20Store%20Images%20-%201%20(1).png)
Understanding and managing the indirect costs of meetings is crucial for any organization aiming to enhance efficiency and productivity. Indirect costs, such as employee downtime, travel and accommodation expenses, regulatory costs, and the impact on employee morale, can significantly affect an organization's bottom line if not properly addressed. Identify your indirect meeting costs with Flowtrace today.
Understanding and managing company meeting costs is essential for organizational efficiency and financial health. Explore the impact of direct,...
Calculate meeting costs with this interactive meeting cost calculator giving you an accurate representation of how much money your meetings are...
Calculate meeting costs and reduce the $37 billion wasted annually on unnecessary meetings. Free calculator tool plus strategies to optimize meeting...